|
Different MRI scanners produce images with different characteristics which leads to an increase in non-biological noise when the images are pooled. This is known as the harmonisation problem. We propose to model harmonisation as a domain adaptation problem, and have proposed a number of methods to enable models to be trained with data from a range of scanners. Home / Harmonisation / Segmentation / Translation / Privacy / Explainable AI |
|
|
|
|
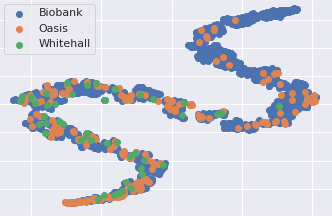
Nicola K Dinsdale, Mark Jenkinson, Ana IL Namburete bioRxiv, 2024 Project Page / Paper / Code We, therefore, propose UniFed, a unified federated harmoni- sation framework, which enables three key processes to be completed: 1) the training of a federated partially labelled harmonisation network, 2) the selection of the most appropriate pretrained model for a new unseen site, and 3) the incorporation of a new site into the harmonised federation. |
|
Nicola K Dinsdale , Mark Jenkinson, Ana IL Namburete ICCV, 2023 Project Page / Paper / Code We propose an Unsupervised Source-Free Domain Adaptation (SFDA) method, SFHarmony, and demonstrate the approach for classification, regression and segmentation tasks. |
|
Nicola K Dinsdale , Mark Jenkinson, Ana IL Namburete MICCAI 2022, 2022 [Early Acceptance] Project Page / Paper / Code Adapted my harmonisation framework to work in a distributed setting, through modelling site features as Gaussian distributions. |
|
Vaanathi Sundaresan, Nicola K Dinsdale, Ludovica Griffanti, Mark Jenkinson, ISBI 2022 [Oral Presentation] Project Page / Paper / Code Exploring the use of omni-supervised learning for white matter hyperintensity segmentation, using age prediction as the selection criteria. Leads to significant increase in sensitivity especially for small lesions. |
|
Nicola K Dinsdale , Mark Jenkinson, Ana IL Namburete Neuroimage, 2021 Project Page / Paper / Code IDP harmonisation using iterative unlearning framework, applied across tasks and architectures. Parts of this work were presented at MIUA 2020 and MICCAI 2020 [Early Acceptance]. |

|
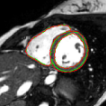
Vaanathi Sundaresan, Giovanna Zamboni, Nicola K Dinsdale , Peter Rothwell, Ludovica Griffanti, Mark Jenkinson Medical Image Analysis 2021 Paper / Code Comparison of DA methods for white matter hyperintensity segmentation, comparing methods including my proposed method: paper. |
|
Jorge Corral Acero, Vaanathi Sundaresan, Nicola K Dinsdale , Vicente Grau, Mark Jenkinson STACOM 2020 - 6th place Paper Segmentation of cardiac MRI across sites, using the method proposed in my paper |

|
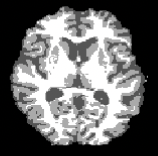
Nicola K Dinsdale , Mark Jenkinson, Ana IL Namburete MICCAI, 2020 [Early Acceptance] Paper / Code MRI harmonisation using iterative unlearning framework, explored for age prediction. |
|
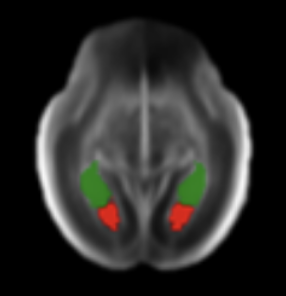
Nicola K Dinsdale , Mark Jenkinson, Ana IL Namburete MIUA, 2020 Paper / Code MRI harmonisation using iterative unlearning framework, explored for segmentation tasks. |
|
Joshua Omolegan, Pak Hei Yeung, Madeleine K Wyburd, Linde Hesse, Monique Haak, Intergrowth Consortium, Ana IL Namburete, Nicola K Dinsdale ISBI 2025 Paper / Code Test time adaptation for robust subcortical segmentation in fetal ultrasound |
The template of this webpage is from source code.